40 - Digital Forensics
Digital forensics is a process for uncovering and interpreting electronic data. The goal of the process is to preserve any evidence from a presumed crime scene in its most original form while performing a structured investigation to reconstruct past events. Digital forensics investigation aims to build an overall picture of a cyber attack based on digital artifacts, namely the traces left by cybercriminals on information systems.
Digital forensics investigation seeks to find the answers to the ultimate questions of the event about 1) What happened, 2) Who was involved, 3) When did it take place, 4) Where did it take place, 5) Why did take place, and 6) How did an incident occur. Answering these questions leads to confirming or refuting allegations of an incident. Digital forensics investigation can also support the mitigation of damages and maturing of future prevention approaches.
Digital forensics investigation consists of different stages and tasks to be performed in connection with them. One common way to describe the course of an IT investigation on a high-level is to divide it into four main stages according to the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST). Each of the steps seeks to take the investigation forward and bring clarity to the open questions regarding the event. The step-by-step progression of an IT investigation from its inception to the conclusion is illustrated in the figure below (Figure 1).
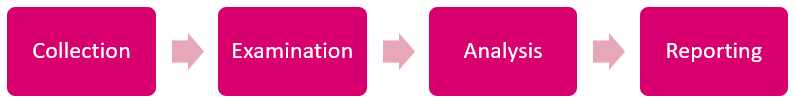 Figure 1. Digital forensics process proposed by NIST
Figure 1. Digital forensics process proposed by NIST
Collection as the first stage in an IT investigation aims to identify all potential sources of information for the event and to collect the data stored in them. The data to be collected will be marked in such a way that it can be subsequently identified and traced to its original source. Data is protected from unauthorized use and uncontrolled alteration throughout its retention period. Improper storage of evidence can reduce the probative value of the data.
The examination stage as the second step seeks to filter out information relevant to the event from the data acquired in the collection stage, while taking care of the integrity of the information. Existing knowledge on both indicators of compromise and indicators of attack, and digital artifacts categories can be used to identify information relevant to the event. The categories bring together the digital traces that a particular type of activity normally produces in information systems.
The goal of the analysis stage is to form an overall picture of the course of an event by assembling the artifacts in a logical order according to the assumed cyber kill chain. As a result of the analysis phase, the ultimate questions of the event are expected to be answered . Sometimes the analysis stage can be confronted with a situation where a final or partial conclusion cannot be drawn. However, the decision to suspend the investigation without result is now justified.
Reporting as the final stage of an IT investigation seeks to document the results of the analysis stage and the ways in which the conclusions of the investigation have been reached. The digital forensics report contains a detailed description of the methods and tools used in the investigation. Through the digital forensics report, it is possible to return retroactively to the investigation to examine the correctness of the actions taken and the results obtained.