50 - Basics of auditing
So, what is auditing? It depends on from which point of view it is considered. If we are looking at auditing from accounting view, the main task is that accounts are in order and in compliance with the law. From the cybersecurity point of view, auditing is about measuring something against a standard. The main purpose here is to get an accurate snapshot. Audit can also be defined as a systematic, independent and documented process for acquiring and reviewing objective evidence, where the objective evidence is all such information that is related to the audit criteria and whose existence can be verified. Audit results are objective estimates of activity and compliance.
In summary, we can state that auditing is a method of seeking evidence whether everything is fine or not.
NIST defines auditing like
Independent review and examination of records and activities to assess the adequacy of system controls, to ensure compliance with established policies and operational procedures, and to recommend necessary changes in controls, policies, or procedures. Source: NIST Glossary
Why we need Auditing
Today, every company is a potential cyber attack target. We cannot assume that criminals are not interested in us. Almost every day we can read news that some company has been hacked or customer data has leaked on the internet. When this happens, the impact on company's business is critical. For example, criminals are hacking into an online store. How will this affect their customers? Will the company lose the customers?
-
Facebook
- When: September 2019
- How many: 419 million records affected
- What: Several unprotected databases were found to contain the phone numbers of around 20% of all Facebook users, in some cases with names and locations
- Reason: The databases were found on a server and had no password protections in place, which meant they were freely accessible to anyone with an internet connection.
- Source: 09.05.2019, FastCompany: The phone numbers of 419 million Facebook accounts have been leaked
-
Microsoft
- When: January 2020
- How many: 250 million records affected
- What: Customer support reconds spanning 14 years were left online without password protection
- Reason: Unsecured Elasticsearch servers contained records spanning a period from 2005 right through to December 2019
- Source: 22.01.2020, Forbes: Microsoft Security Shocker As 250 Million Customer Records Exposed Online
-
Canva
- When: May 2018
- How many: 139 million records affected
- What: Stolen data included details such as customer usernames, real names, email addresses, and city & country information, where available.
- Reason: Hacking
- Source: 24.05.2019, ZDNet: Australian tech unicorn Canva suffers security breach
So, if we look at the cases above, could we have minimized the damage by auditing the environments? One of the purposes of auditing is that we will find these threats before someone else finds them. You can find more information about this on this beautiful website World's Biggest Data Breaches & Hacks
Information security and privacy
These terms are important when auditing organization systems, because systems always contain information and usually this information is under NDA (non-disclosure agreement). Information can be for example product information or customer database, which includes a privacy point of view. So, every time we must decide what we can do and what not.
NIST defines information security
The protection of information and systems from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruption, modification, or destruction in order to provide confidentiality, integrity, and availability.
Source: NIST Glossary
Usually Information security is demonstrated with the CIA triad. It describes how these three points are connected with each other and if one is broken, information is compromised.
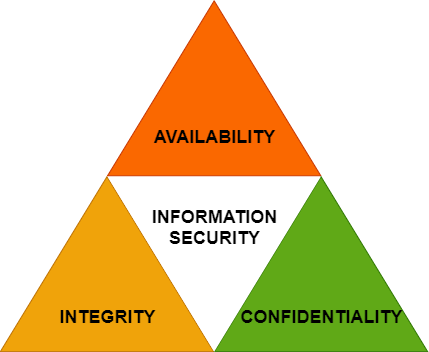
Hospital patient information system is an easy way to explain this CIA triad in practice.
- Confidentiality through preventing access by unauthorized users.
- for example, if someone else can read your patient information, confidentiality is broken
- Integrity from validating that your data is trustworthy and accurate.
- for example, if someone else can change your patient information, integrity is broken
- Availability by ensuring data is available when needed.
- for example, if in a treatment situation a doctor cannot access the system, availability is broken
Terminology
Information security always contains a rather great amount of terminology and abbreviations, for example: hash, ISMS, data mining, pen test, spoofing. Below are listed some good pages, where you can find explanations for these terms. You can also use Google to find the needed information.
Legislation & Regulations
When we are auditing information systems, we must follow legislation and regulations. Usually the audit is carried out for the client, and then these things must be recorded in the contract. For example, driving a car is not illegal, but if you take someone’s car without permission, you are breaking the law.
There is national and international legislation. Usually this legislation is country specific, so this guide does not take a detailed position on this.
Best example on European Union regulations is General Data Protection Regulation 2016/679. This main purpose of this regulation is to protect EU citizens from how the companies are using their information. For example, this regulation allows a person to request from the company all the information that has been stored about them. The GDPR defines an array of legal terms at length. Below are some of the most important ones:
-
Personal data — Personal data is any information that relates to an individual who can be directly or indirectly identified. Names and email addresses are obviously personal data. Location information, ethnicity, gender, biometric data, religious beliefs, web cookies, and political opinions can also be personal data. Pseudonymous data can also fall under the definition if it is relatively easy to ID someone from it.
-
Data processing — Any action performed on data, whether automated or manual. The examples cited in the text include collecting, recording, organizing, structuring, storing, using, erasing… so basically anything.
-
Data subject — The person whose data is processed. These are your customers or site visitors.
-
Data controller — The person who decides why and how personal data will be processed. If you are an owner or employee in your organization who handles data, this is you.
-
Data processor — A third party that processes personal data on behalf of a data controller. The GDPR has special rules for these individuals and organizations. They could include cloud servers e.g. Tresorit or email service providers like ProtonMail.
Legislation exists to enforce the need for companies to understand the “whole of business.” Financial institutions must now be able to report on all accounts/instruments their customers have and all transactions against those accounts/instruments, including any suspicious transaction patterns.
Standards
Standardization means creating agreed ways of doing something to simplify the work of authorities, facilitate trade, and to make consumers' everyday lives easier.
- Standard means a technical specification, adopted by a recognized standardization body, for repeated or continuous application, with which compliance is not compulsory.
- Technical specification means a document that prescribes technical requirements to be fulfilled by a product, process, service, or system.
CEN European Committee for Standardization is one community that has done many standardizations on cybersecurity. The main task has been CEN/CLC/JTC 13 - Cybersecurity and Data Protection, which includes almost twenty ISO standards on this subject area.
- EN ISO/IEC 18045:2020, Methodology for IT security evaluation (ISO/IEC 18045:2008)
- EN ISO/IEC 27037:2016, Guidelines for identification, collection, acquisition and preservation of digital evidence (ISO/IEC 27037:2012)
- EN ISO/IEC 27042:2016, Guidelines for the analysis and interpretation of digital evidence (ISO/IEC 27042:2015)
- EN ISO/IEC 29147:2020, Vulnerability disclosure (ISO/IEC 29147:2018)
- EN ISO/IEC 30111:2020, Vulnerability handling processes (ISO/IEC 30111:2019)
- and so on...
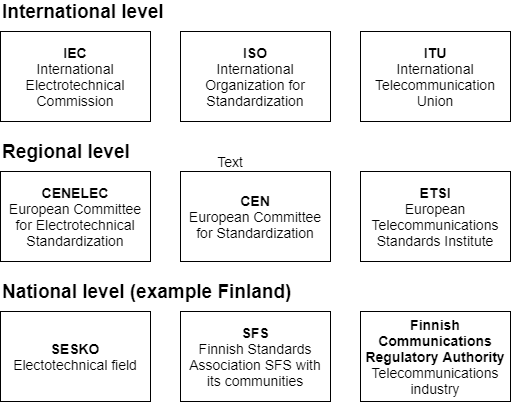
Standardization levels can also be split into three different categories (International, Regional, National level) as shown in the Figure below.
There are also other standards such as PCI DSS (The Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard) and PA-DSS (The PCI Payment Application Data Security Standard) which are targeting a specific area.